Transform CBAM into Competitive Advantage
Calculate emissions, automatically generate CBAM reports,
and gain data-driven insights into your supply chain.
Importers
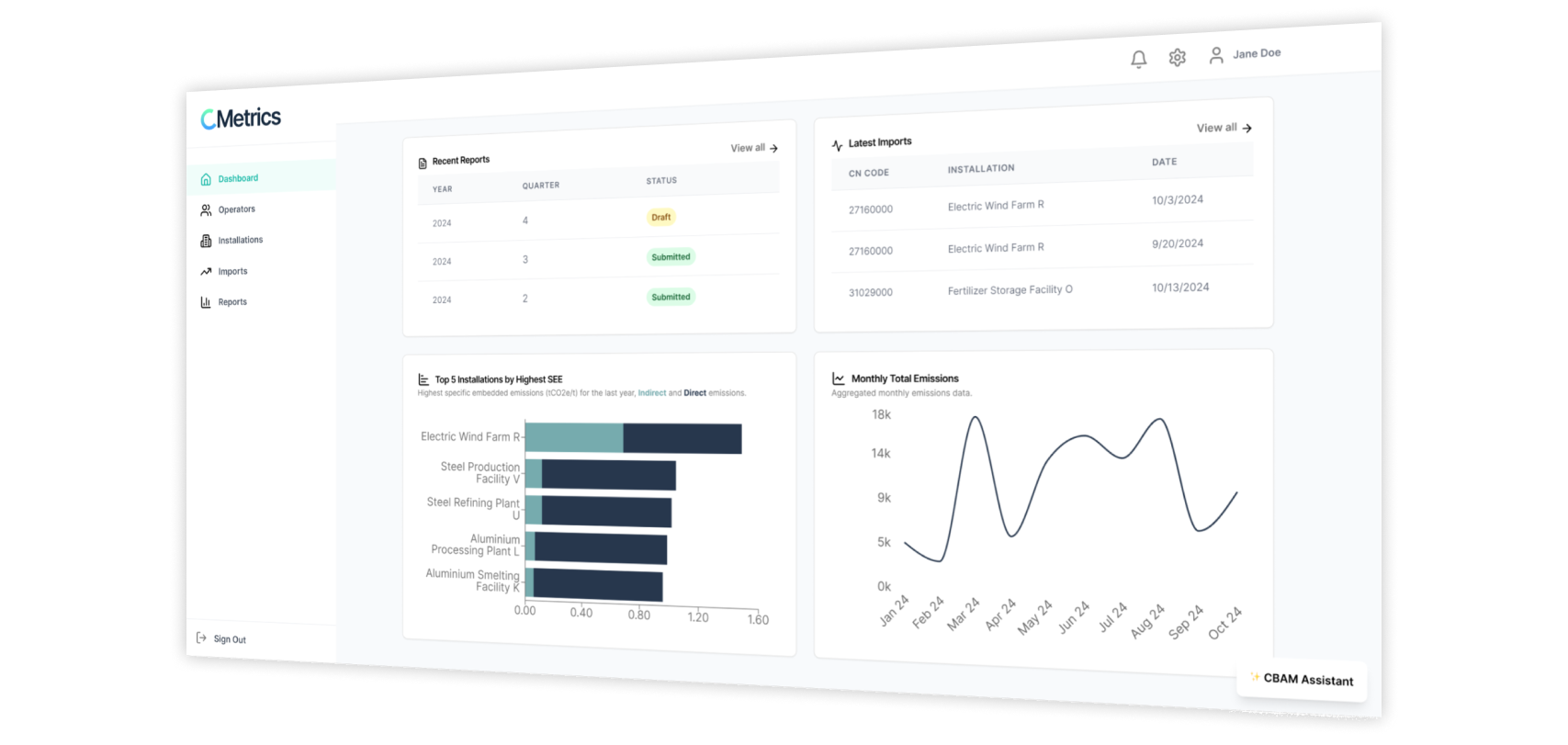
Streamlined Data Collection & Instant CBAM Reporting
C-Metrics transforms complex production processes into fully automated, CBAM-compliant reports in minutes, reducing compliance workload by 70% while ensuring accuracy and regulatory alignment.
Suppliers
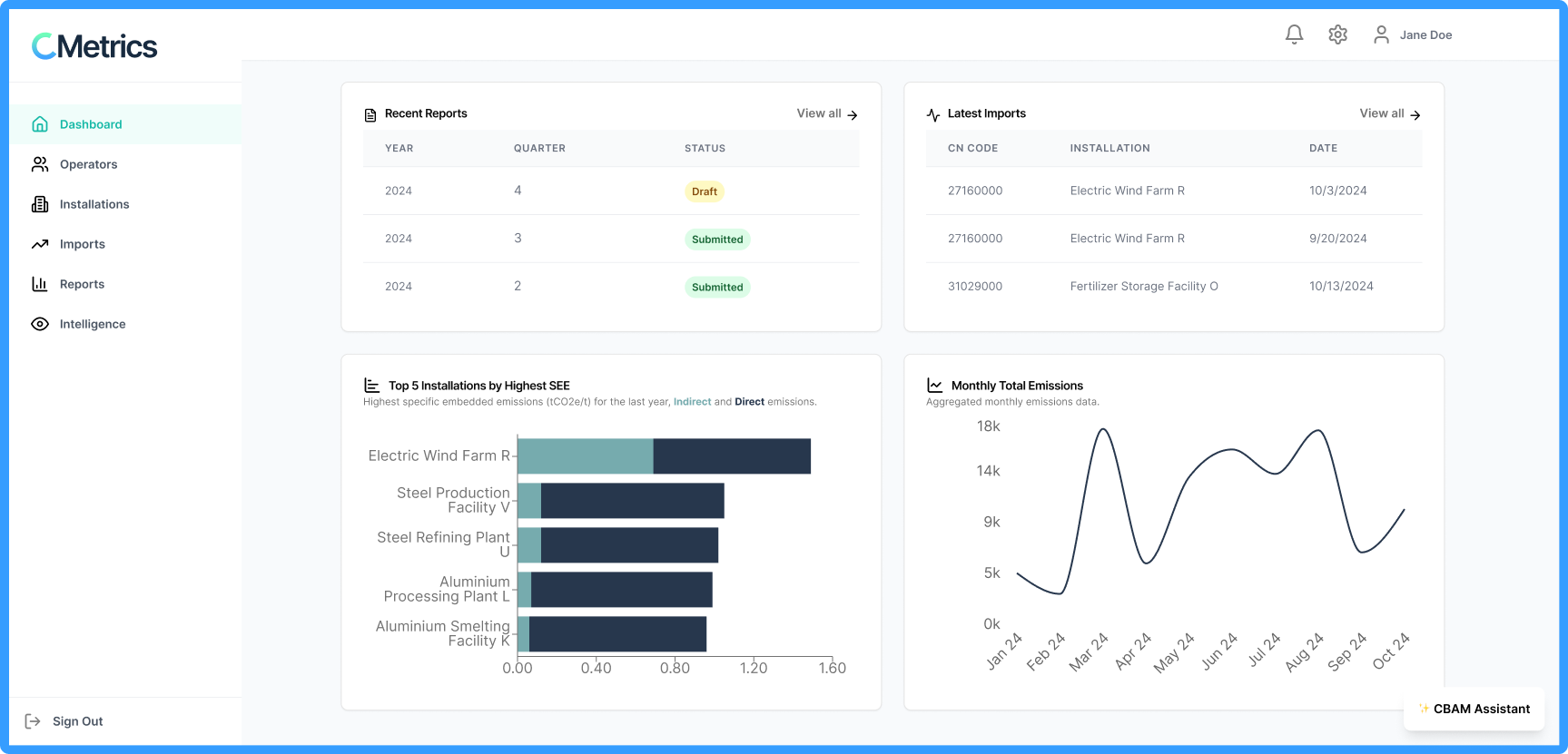
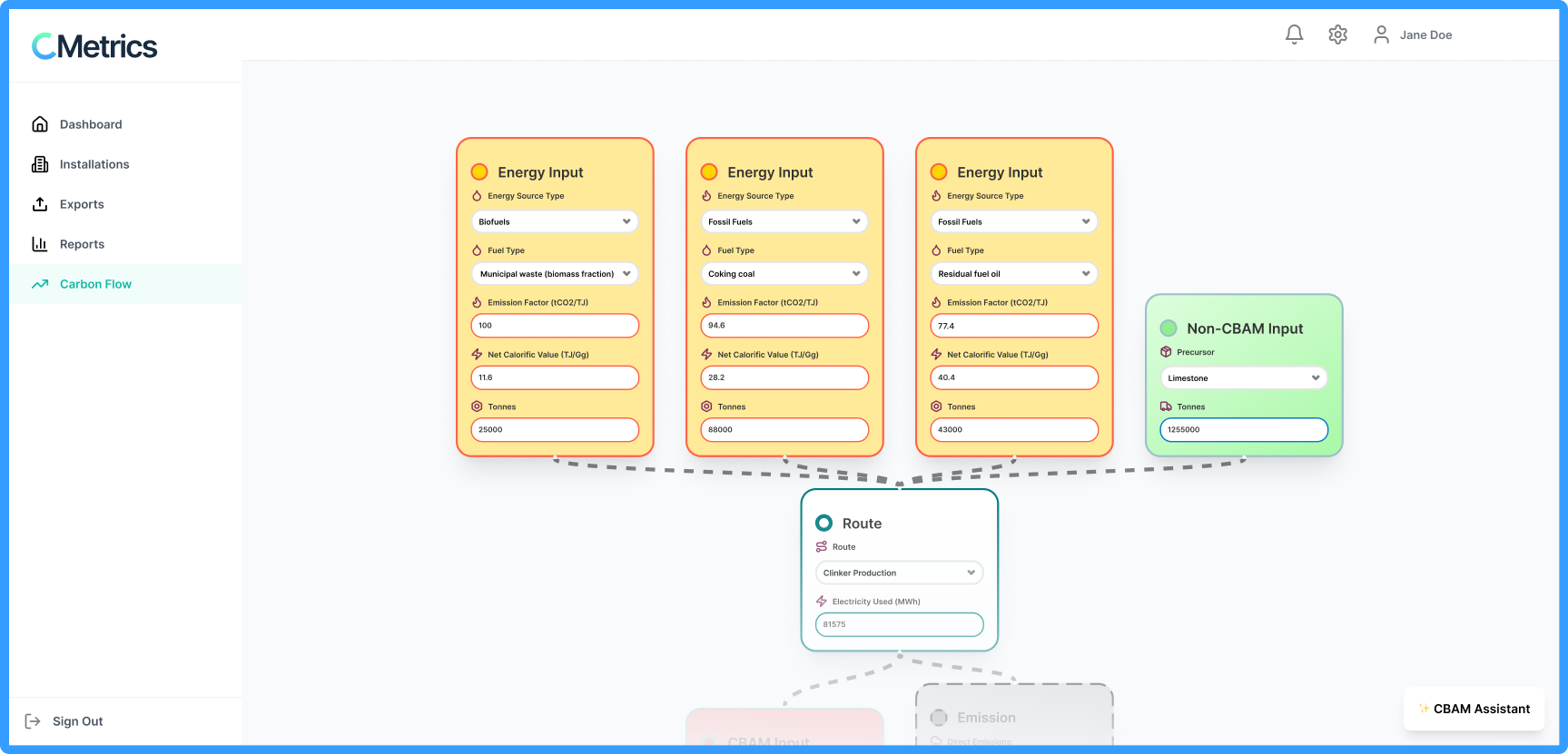
Carbon footprint tracking and optimization
Map your production processes visually, monitor carbon flows at each stage, and effortlessly generate and securely share emissions data with your importers. No carbon accounting expertise or ugly excel sheets required.
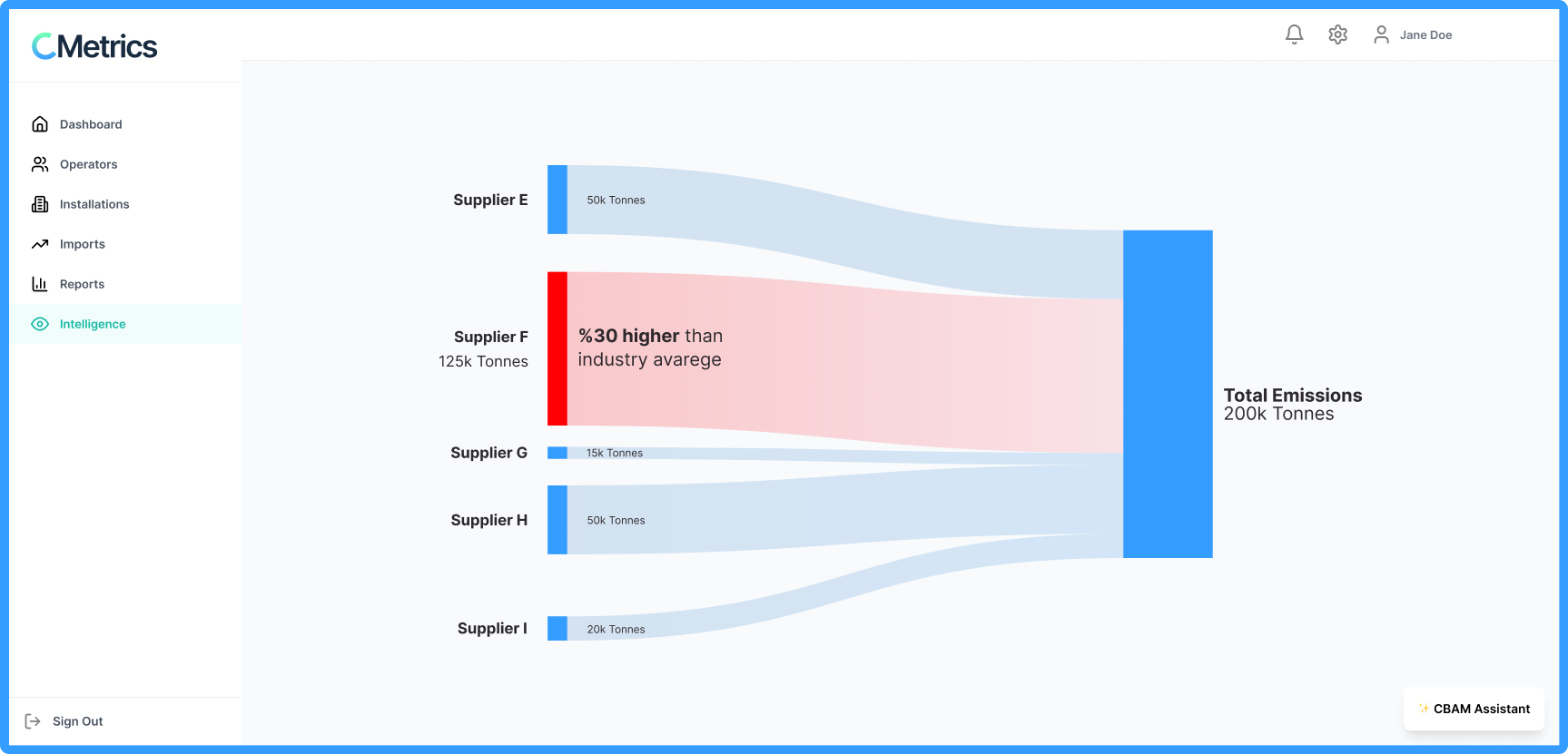
Competitiveness Insights
Supply chain optimization by using data insights
C-Metrics analyzes your trade data to optimize supply chain costs and carbon efficiency, helping you stay competitive in carbon-regulated markets.
Representative Agents
Complete Solutions for Agents Serving All Client Types
- Comprehensive Importer & Exporter Tracking
- Simplified Supplier Emissions Calculations
- Automated Emissions and CBAM Reporting

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)?
The Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) is a climate action policy implemented by the European Union (EU). The main goal of CBAM is to prevent carbon leakage, which happens when EU companies move carbon-intensive production to countries with less stringent emission rules. This leads to increased greenhouse gas emissions globally. CBAM addresses this issue by putting a price on the carbon content of certain imported goods.
What goods are covered by CBAM?
During the transitional phase, CBAM applies to imports of goods from the following sectors:
- Cement (cement clinkers, white Portland cement, other Portland cement, aluminous cement, and other hydraulic cements)
- Electricity
- Fertiliser (nitric acid and sulphonitric acids)
- Iron and steel (various iron and steel products)
- Aluminium (unwrought aluminium and various aluminium products)
- Chemicals (hydrogen)
Which CN codes are covered under the EU CBAM Regulation?
Cement
- 2507 00 80 – Other kaolinic clays (Calcined clay)
- 2523 10 00 – Cement clinkers
- 2523 21 00 – White Portland cement, whether or not artificially coloured
- 2523 29 00 – Other Portland cement
- 2523 90 00 – Other hydraulic cements
- 2523 30 00 – Aluminous cement
Electricity
- 2716 00 00 – Electrical energy
Fertiliser
- 2808 00 00 – Nitric acid; sulphonitric acids
- 3102 10 – Urea, whether or not in aqueous solution
- 2814 – Ammonia, anhydrous or in aqueous solution
- 2834 21 00 – Nitrates of potassium
- 3102 – Mineral or chemical fertilisers, nitrogenous (except 3102 10 – Urea)
- 3105 – Mineral or chemical fertilisers containing two or three of the fertilising elements nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium; other fertilisers
- Except: 3105 60 00 – Mineral or chemical fertilisers containing the two fertilising elements phosphorus and potassium
Iron and Steel
- 2601 12 00 – Agglomerated iron ores and concentrates, other than roasted iron pyrites
- 7201 – Pig iron and spiegeleisen in pigs, blocks, or other primary forms
- 7202 1 – Ferro-manganese
- 7202 4 – Ferro-chromium
- 7202 6 – Ferro-nickel
- 7203 – Ferrous products obtained by direct reduction of iron ore and other spongy ferrous products
- 7205 – Granules and powders, of pig iron, spiegeleisen, iron or steel (if not covered under category pig iron)
- 7206 – Iron and non-alloy steel in ingots or other primary forms (excluding iron of heading 7203)
- 7207 – Semi-finished products of iron or non-alloy steel
- 7218 – Stainless steel in ingots or other primary forms; semi-finished products of stainless steel
- 7224 – Other alloy steel in ingots or other primary forms; semi-finished products of other alloy steel
- 7208 – Flat-rolled products of iron or non-alloy steel, of a width of 600 mm or more, hot-rolled, not clad, plated or coated
- 7209 – Flat-rolled products of iron or non-alloy steel, of a width of 600 mm or more, cold-rolled (cold-reduced), not clad, plated or coated
- 7210 – Flat-rolled products of iron or non-alloy steel, of a width of 600 mm or more, clad, plated or coated
- 7211 – Flat-rolled products of iron or non-alloy steel, of a width of less than 600 mm, not clad, plated or coated
- 7212 – Flat-rolled products of iron or non-alloy steel, of a width of less than 600 mm, clad, plated or coated
- 7213 – Bars and rods, hot-rolled, in irregularly wound coils, of iron or non-alloy steel
- 7214 – Other bars and rods of iron or non-alloy steel, not further worked than forged, hot-rolled, hot-drawn or hot-extruded, but including those twisted after rolling
- 7215 – Other bars and rods of iron or non-alloy steel
- 7216 – Angles, shapes and sections of iron or non-alloy steel
- 7217 – Wire of iron or non-alloy steel
- 7219 – Flat-rolled products of stainless steel, of a width of 600 mm or more
- 7220 – Flat-rolled products of stainless steel, of a width of less than 600 mm
- 7221 – Bars and rods, hot-rolled, in irregularly wound coils, of stainless steel
- 7222 – Other bars and rods of stainless steel; angles, shapes and sections of stainless steel
- 7223 – Wire of stainless steel
- 7225 – Flat-rolled products of other alloy steel, of a width of 600 mm or more
- 7226 – Flat-rolled products of other alloy steel, of a width of less than 600 mm
- 7227 – Bars and rods, hot-rolled, in irregularly wound coils, of other alloy steel
- 7228 – Other bars and rods of other alloy steel; angles, shapes and sections, of other alloy steel; hollow drill bars and rods, of alloy or non-alloy steel
- 7229 – Wire of other alloy steel
- 7301 – Sheet piling of iron or steel, whether or not drilled, punched or made from assembled elements; welded angles, shapes and sections, of iron or steel
- 7302 – Railway or tramway track construction material of iron or steel
- 7303 – Tubes, pipes and hollow profiles, of cast iron
- 7304 – Tubes, pipes and hollow profiles, seamless, of iron (other than cast iron) or steel
- 7305 – Other tubes and pipes (for example, welded, riveted or similarly closed), having circular cross-sections, the external diameter of which exceeds 406,4 mm, of iron or steel
- 7306 – Other tubes, pipes and hollow profiles (for example, open seam or welded, riveted or similarly closed), of iron or steel
- 7307 – Tube or pipe fittings (for example, couplings, elbows, sleeves), of iron or steel
- 7308 – Structures and parts of structures, of iron or steel
- 7309 – Reservoirs, tanks, vats and similar containers for any material, of iron or steel, of a capacity exceeding 300 l
- 7310 – Tanks, casks, drums, cans, boxes and similar containers, for any material, of iron or steel, of a capacity not exceeding 300 l
- 7311 – Containers for compressed or liquefied gas, of iron or steel
- 7318 – Screws, bolts, nuts, coach screws, screw hooks, rivets, cotters, cotter pins, washers and similar articles, of iron or steel
- 7326 – Other articles of iron or steel
Aluminium
- 7601 – Unwrought aluminium
- 7603 – Aluminium powders and flakes
- 7604 – Aluminium bars, rods and profiles
- 7605 – Aluminium wire
- 7606 – Aluminium plates, sheets and strip, of a thickness exceeding 0,2 mm
- 7607 – Aluminium foil (whether or not printed or backed with paper, paperboard, plastics or similar backing materials) of a thickness not exceeding 0,2 mm
- 7608 – Aluminium tubes and pipes
- 7609 00 00 – Aluminium tube or pipe fittings (for example, couplings, elbows, sleeves)
- 7610 – Aluminium structures and parts of structures
- 7611 00 00 – Aluminium reservoirs, tanks, vats and similar containers, for any material, of a capacity exceeding 300 litres
- 7612 – Aluminium casks, drums, cans, boxes and similar containers, of a capacity not exceeding 300 litres
- 7613 00 00 – Aluminium containers for compressed or liquefied gas
- 7614 – Stranded wire, cables, plaited bands and the like, of aluminium, not electrically insulated
- 7616 – Other articles of aluminium
Chemicals
- 2804 10 000 – Hydrogen
Note: This list includes greenhouse gases monitored for each category as specified in Annex I to Regulation (EU) 2023/956.
Which countries does CBAM apply to?
CBAM applies to goods imported from any country outside of the EU that doesn’t have an equivalent carbon pricing system. However, it does not apply to goods originating from Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland. Some specific territories are also exempt, including Büsingen, Heligoland, Livigno, Ceuta, and Melilla.
How are emissions calculated under CBAM?
Emissions under CBAM are calculated based on the embedded emissions of the imported goods. This refers to the greenhouse gases emitted during the entire production process, including both direct and indirect emissions.
- Direct emissions come directly from the production process itself.
- Indirect emissions come from the generation of electricity consumed during the production process.
There are two methodologies for determining embedded emissions:
Measurement-based methodology: This involves directly measuring emissions from the production process.
Calculation-based methodology: This involves calculating emissions based on the amount and type of materials and fuels used in the production process, along with relevant emission factors.
What are default values and how are they used in CBAM?
During the CBAM transitional phase, importers can use default values provided by the EU to determine the embedded emissions of imported goods. These default values represent the average emission intensity of goods produced in different countries. Importers are encouraged to transition towards providing actual emissions data over time.
How does the "bubble approach" work for determining emissions?
The “bubble approach” allows operators to define one joint production process for monitoring and reporting embedded emissions when multiple CBAM goods are produced within the same installation. This simplifies the monitoring process and reduces administrative burden. This approach can be used for goods in the iron and steel sector and the aluminium sector.
How is CBAM data reported?
Importers are required to submit CBAM declarations to their national authorities, detailing the embedded emissions of their imported goods. The declaration must include information such as:
- Description of the goods
- Combined Nomenclature (CN) code
- Quantity of goods imported
- Embedded emissions of the goods
- Country of origin
How does CBAM interact with the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS)?
CBAM complements the EU ETS by ensuring that imports of carbon-intensive goods face a similar carbon price as goods produced within the EU. This helps create a level playing field and prevents carbon leakage.